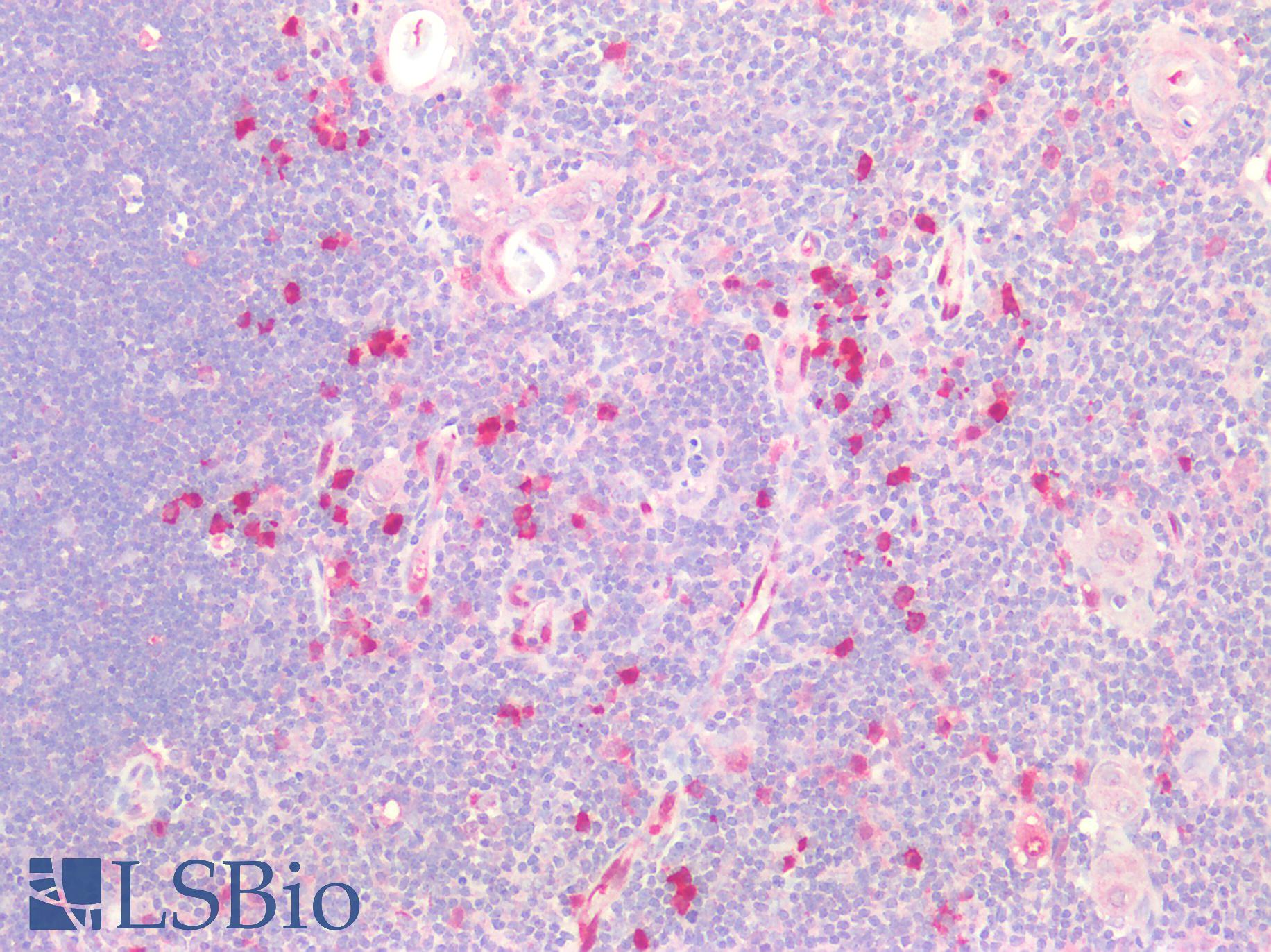
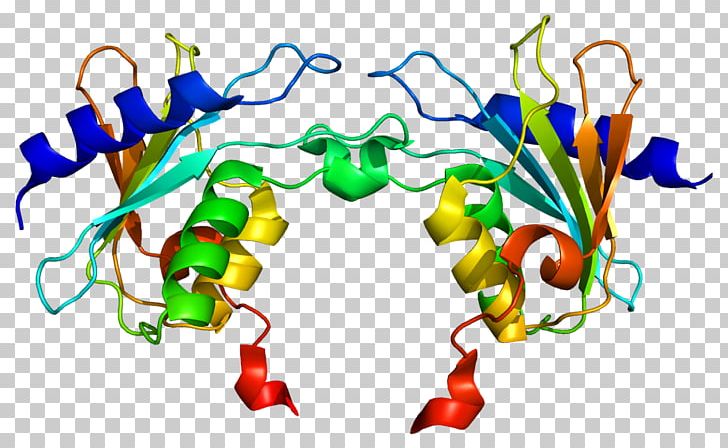
Cytidine deaminase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDA gene.
This gene encodes an enzyme involved in pyrimidine salvaging. The encoded protein forms a homotetramer that catalyzes the irreversible hydrolytic deamination of cytidine and deoxycytidine to uridine and deoxyuridine, respectively. It is one of several deaminases responsible for maintaining the cellular pyrimidine pool. Mutations in this gene are associated with decreased sensitivity to the cytosine nucleoside analogue cytosine arabinoside used in the treatment of certain childhood leukemias. Most cytidine deaminases act on RNA, and the few that act on DNA require ssDNA.
A related activation-induced (cytidine) deaminase (AID) regulates antibody diversification, especially the process of somatic hypermutation.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.
References
Further reading
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P32320 (Cytidine deaminase) at the PDBe-KB.