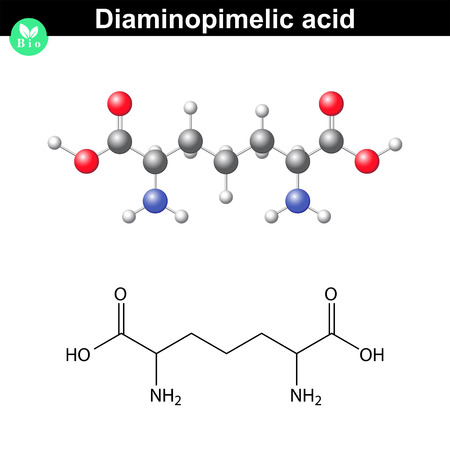
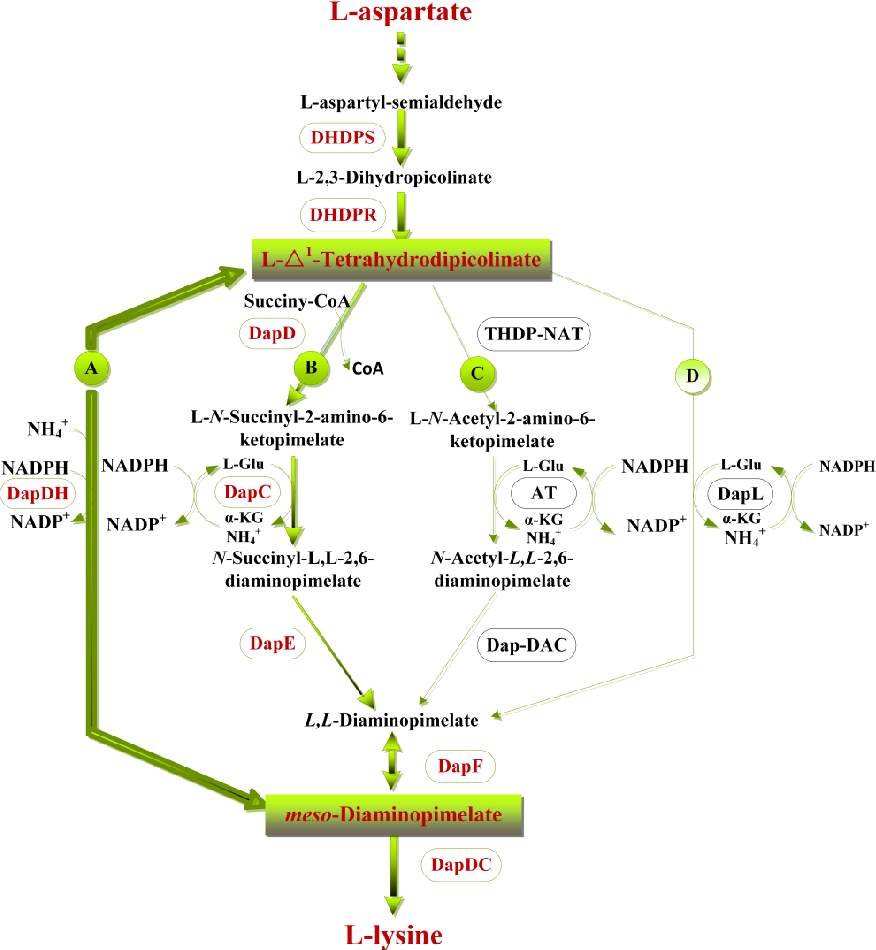
Diaminopimelic acid (DAP) is an amino acid, representing an epsilon-carboxy derivative of lysine. meso-α,ε-Diaminopimelic acid is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of lysine and undergoes decarboxylation by diaminopimelate decarboxylase to give the final product.
DAP is a characteristic of certain cell walls of some bacteria. DAP is often found in the peptide linkages of NAM-NAG chains that make up the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. When provided, they exhibit normal growth. When in deficiency, they still grow but with the inability to make new cell wall peptidoglycan.
This is also the attachment point for Braun's lipoprotein.
See also
- Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in DAP synthesis
- Peptidoglycan
- Pimelic acid
Images
References